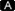Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Lok Sabha Debates
- Historical Debates
- Parliamentary Documents
- Publications
Part 1 comprises of questions asked by Members of Parliament and answered by the concerned Ministers. The first Hour of a sitting of Lok Sabha is devoted to Questions and is called the Question Hour. For each sitting, 20 Starred (Oral) and 230 Unstarred (Written) Questions are listed and these can be explored title-wise, member-wise and through several other parameters.
Part-2 Other than Questions and Answers is the proceeding of a day and includes debate on Bills, discussion on urgent matters, Statements by Ministers, etc. which takes place after the Question Hour is over. These can be explored by Members, Lok Sabha Number, Debate Type, Title and Date.
Under "Text of Debates" collection, the debate, as printed in the book, of a specific date / session / Lok Sabha stored in pdf A form is displayed. The proceedings of a specific date from 11 am till the house adjourned that day makes it one single file.
"Debate by Titles/Members" collection displays metadata of Lok Sabha debates. Each day's debate has been split title wise to facilitate user to get information of specific member or question type or debate type, etc.
| Lok Sabha Number | Version of Debates |
|---|---|
| 1. | Original |
| 2. | Original |
| 3. | Original |
| 4. | Original |
| 5. | Original |
| 6. | Original |
| 7. | Original |
| 8. | English |
| 9. | English |
| 10. | English |
| 11. | English |
| 12. | English |
| 13. | English |
| 14. | Original |
| 15. | Original |
| 16. | Original |
The Hindi version of Lok Sabha Debates from 8th to 13th Lok Sabha have been digitized and will be uploaded shortly.
- Presidential Addresses
- Budget Speeches
- Parliamentary Committee Reports
- Indian Legislative Council Debates (1858-1920)
- Central Legislative Assembly Debates (1921-1947)
- Council of State Debates (1921 to 1946 )
- Constituent Assembly of India (Draft Making 1946-1950)
- Constituent Assembly of India (Legislative) (1947-1949)
- Debates of Provisional Parliament (1950-1952)
- Books
- Information Bulletins
- Periodicals
Explore is to view the display of a collection in an organized manner. Further, it can be sorted by Lok Sabha number, date, title, member, type, etc. in ascending/ descending order in dictionary format.
Search on the other hand is finding instant results by putting any keyword in the search box from the entire database/ selective collection and further refining it to get specific results through various filter options.
- You can do free search either from one collection or from all the collections of PDL.
- You can have precise searching by putting quotes around text of your search, eg. "Road Transport".
- For precise member's name "B.R. Ambedkar" or "Ambedkar".
- For precise Date "13-05-1952".
- Please ensure that there are no gaps in your text within quotes.
- For more details, please see "User Guide"
"dd.mm.yyyy"(13.05.1952), and "yyyy.mm.dd"(1952.05.13) would produce same results.
Also "dd-mm-yyyy" (13-05-1952) and "yyyy-mm-dd" (1952-05-13) would produce same results.
Even without inverted commas the results would be fetched inclusively.
- Suppose a user has query about Election Commission to be searched from all the collections. So, we type election commission in search box and it will give 8505 search results and discover feature on right side will display the collections wherein word(s) election commission or election or commission occurs. The user query can further be seen in filtered form in DISCOVER feature by title, date, Lok Sabha number, Committee name or debate type. The user can see one by one these results.
- But to make a precise search, type the same search words within inverted quotes like "election commission" in search box and now only 1872 results appear which are in various collections as shown under type
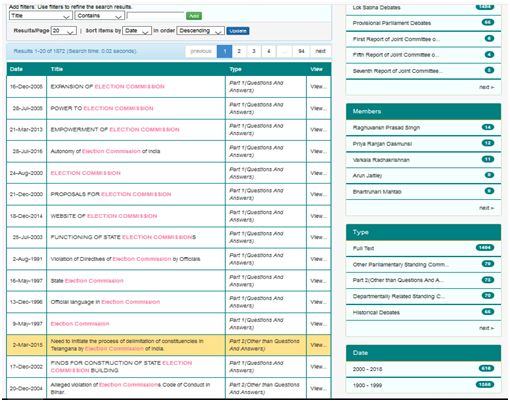
Following example of finding earthquake and its various facets through database by application of various filters will help the user to apply filters in finding the precise information in minimum time.
If we type earthquake in search box it will give 1748 results.
Pl see following search, which with, more use of filters has reduced it from 1748 to 2.
To digitally preserve something is to maintain it over a long period of time.
- The online presentation of the content in an organized tree of Community and Collections is a main feature of DSpace.
- Users can access pages for individual items, these are metadata descriptions together with files available for download.
- Full-text search: DSpace can process uploaded text based contents for full-text searching. This means that not only the metadata you provide for a given file will be searchable, but all of its contents will be indexed as well. This allows users to search for specific keywords that only appear in the actual content and not in the provided description.
- Navigation : DSpace allows users to find their way to relevant content in a number of ways, including:
- Searching for one or more keywords in metadata or extracted full-text
- Faceted browsing through any field provided in the item description. Search is an essential component of discovery in DSpace. Users' expectations from a search engine are quite high, so a goal for DSpace is to supply as many search features as possible.